ESOPHAGEAL AND GASTRIC DISEASES
-
Esophageal Cancer
Esophagus, is a hollow muscular tube (the food pipe) that runs between your throat and the stomach. In esophageal cancer, a malignant tumor forms in the inner lining of the esophagus and then it advances and spreads.
-
Stomach Cancer
Stomach wall is made of five layers of tissue. Stomach cancer begins in the inner most layer, mucus-producing cells that line the stomach. It then advances and spreads.
-
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumour (GIST)
Gastrointestinal stromal tumours are abbreviated as GISTs (pronounced “jists”). These tumours start in the specialized cells of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and differ from other cancers of the GI tract. GISTs most commonly arise in the stomach, followed by the small intestine, but can occur anywhere along the GI tract. The mutations in the KIT gene and PDGFRA gene cause most GISTs.
-
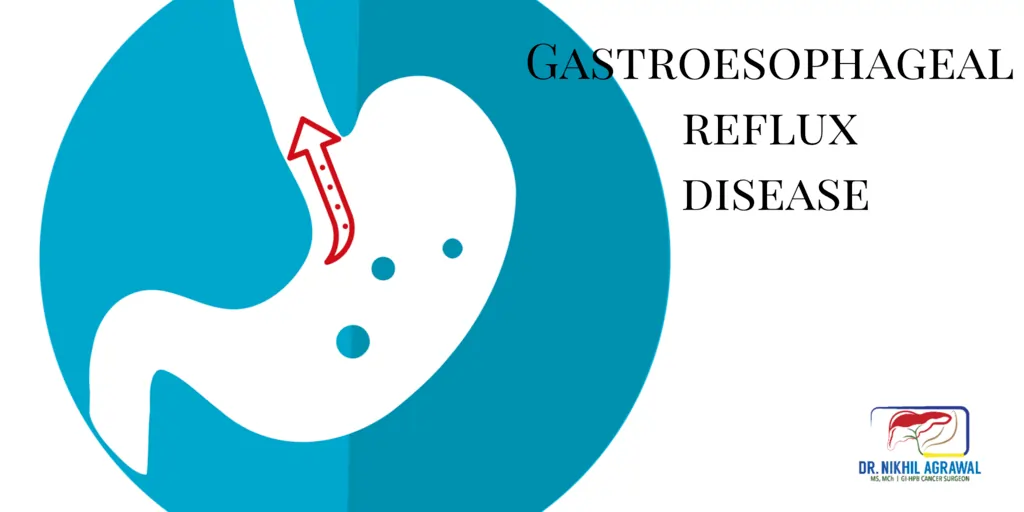
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a digestive disorder that occurs when acidic stomach juices or food and fluids flows back from the stomach into the esophagus. It then irritates the esophageal lining and produces symptoms. It happens when the valve-like mechanism between the stomach and esophagus becomes defective.
-
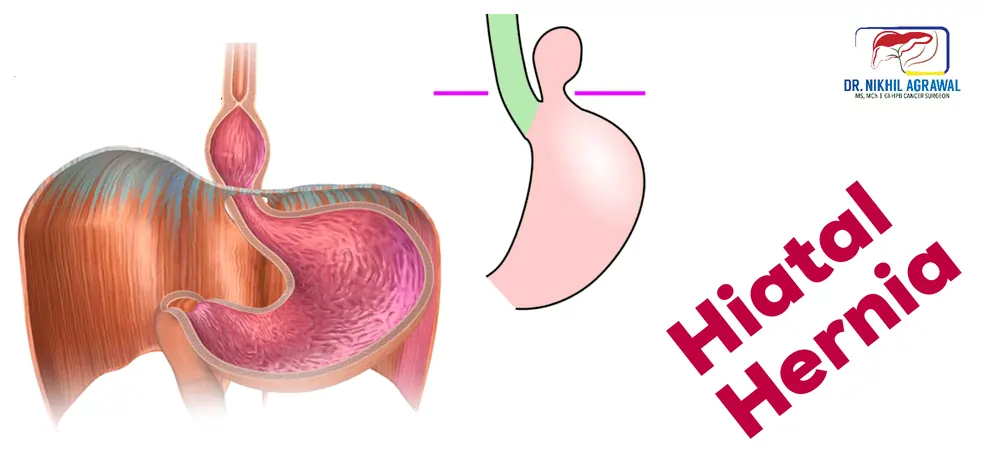
Hiatus Hernia
Hiatus Hernia is a condition in which the upper part of the stomach bulges or squeezes through the opening in the diaphragm (large muscle separating chest and abdomen) into the chest. The opening is where the food pipe (esophagus) passes on its way to the stomach.
-
Achalasia Cardia
Achalasia is a disorder in which food does not easily pass from the esophagus (food pipe) to the stomach. It happens because the valve-like muscles and nerves of the gastroesophageal junction are defective.