PANCREATIC CANCER
Treatment in India
-
What is Pancreas?
The pancreas is a vital organ located in the upper abdomen behind the stomach. It produces hormones, including insulin and glucagon, which help regulate the body's blood sugar levels and metabolism. It also produces enzymes that aid in the digestion of food.
-
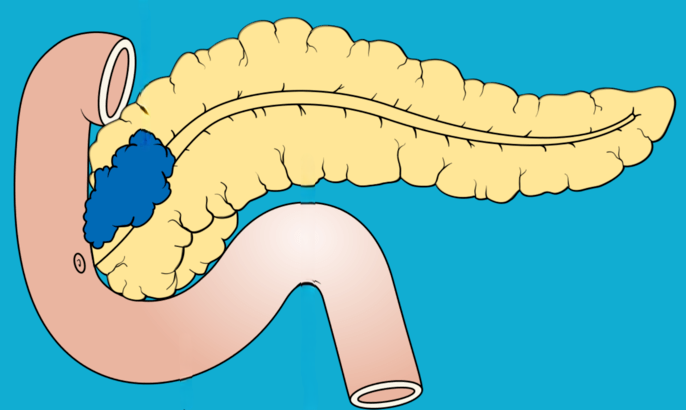
What is pancreatic cancer?
Cancer begins when an error (mutation) occurs in a cell's DNA. The cells then divide and grow uncontrolled. These accumulated cells form cancer. Pancreatic cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the pancreas. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is the most common type of pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatic cancer is the 7th leading cause of cancer-related death.
-

What are signs and symptoms of pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer like most gastrointestinal cancers is asymptomatic in initial stages.
The symptoms include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin, eyes and urine with pale stools)
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Recent onset diabetes
-

What are the risk factors for pancreatic cancer?
Anything that increases the risk of someone getting cancer is a risk factor.
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer are:
- Old age
- Smoking
- Family history or hereditary conditions
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Obesity
-
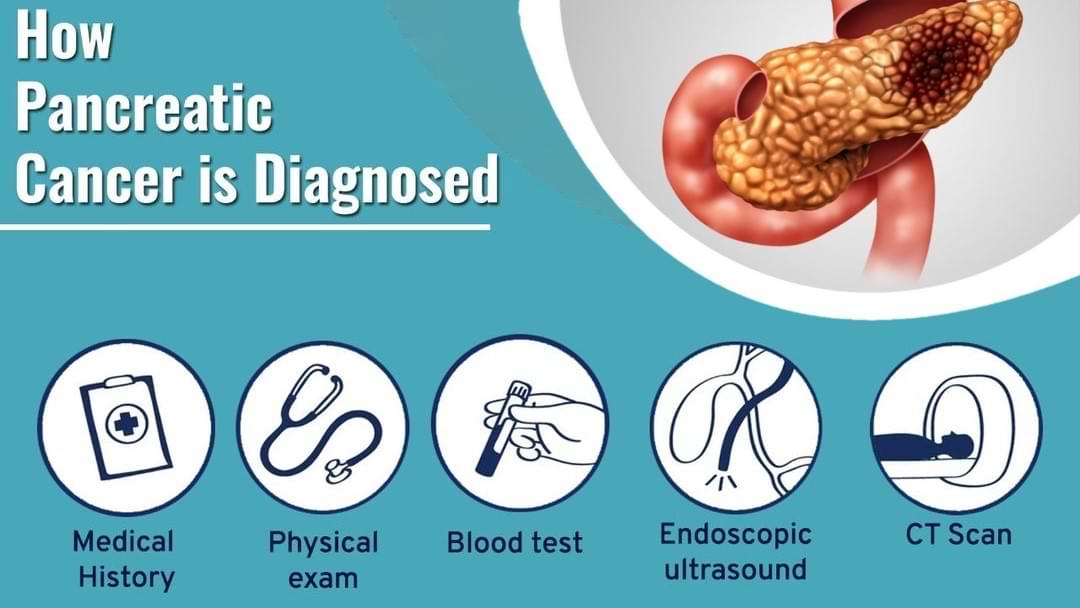
How is pancreatic cancer diagnosed and staged?
Pancreatic cancer is typically diagnosed using a combination of imaging tests, blood tests, and sometimes biopsy. Some common imaging tests used to diagnose pancreatic cancer include computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, and PET-CT scans. Blood tests, such as the CA 19-9 test, can also help diagnose pancreatic cancer. A biopsy, which involves taking a small sample of tissue from the pancreas for analysis, is sometimes used to confirm a pancreatic cancer diagnosis. The doctor may also perform other tests, such as endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) to get a better view of the pancreas and surrounding areas.
Finding the disease's full extent is staging. These images are then used to determine the size and location of the cancer, as well as whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes, blood vessels or other organs.
-

What are the stages of pancreatic cancer?
The stages of pancreatic cancer are:
-
Resectable: The cancer can be removed by surgery.
-
Borderline resectable: The cancer is infiltrating a vital vessel near the pancreas.
-
Locally advanced: The cancer cannot be removed surgically.
-
Metastatic: The cancer has spread to distant organs.
These stages help determine the appropriate treatment plan for pancreatic cancer.
-
-
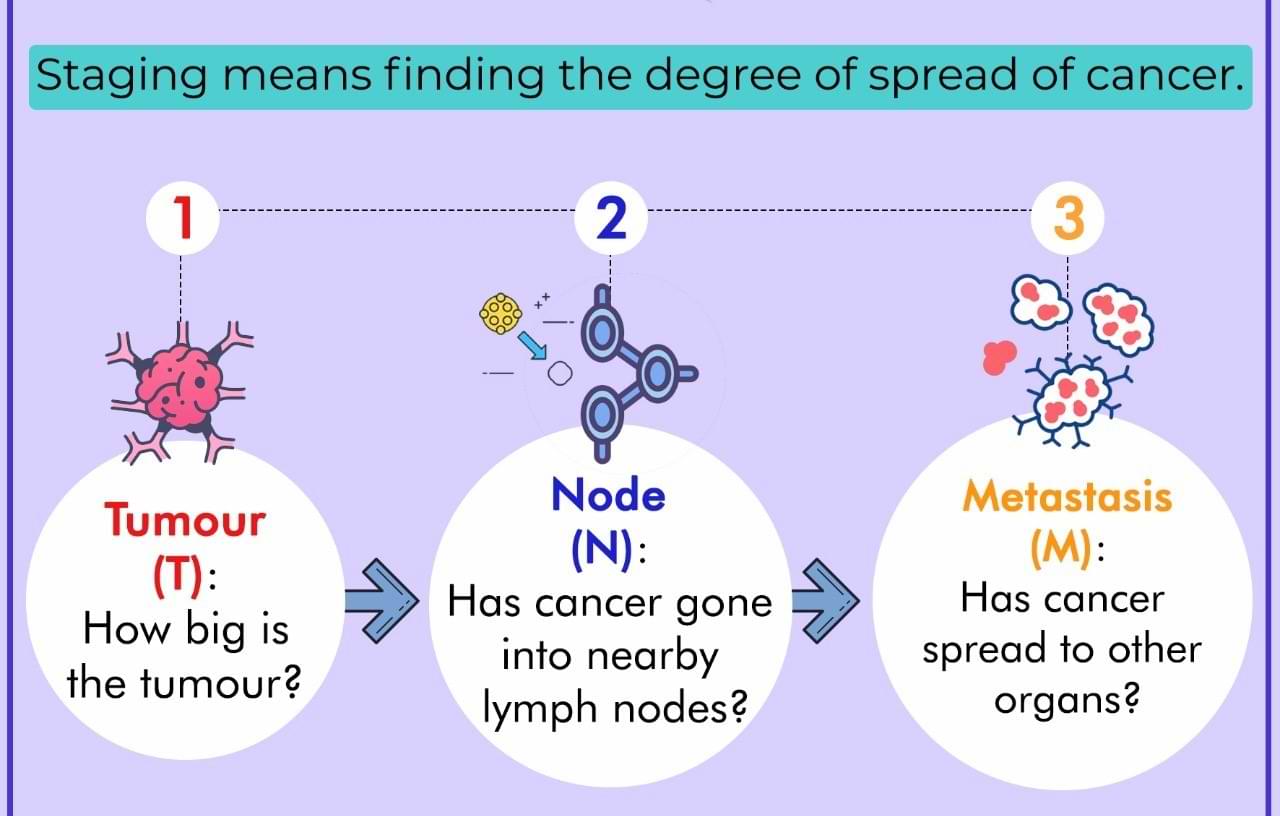
What is TNM staging of pancreatic cancer?
TNM staging is a system used to classify the extent of cancer based on the size and location of the tumor (T), the presence of cancer cells in nearby lymph nodes (N), and the presence of metastasis (M) to distant organs.
Pancreatic cancer stage ranges from I to IV. Chances of recovery from cancer (prognosis) depend on the stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis.
The definite stage is determined after surgery by histopathological examination of the removed cancer specimen. It is called surgical staging. The stage determined after imaging tests is the clinical stage.
-

how is pancreatic cancer treated?
The treatment of pancreatic cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the location and size of the tumor, and the overall health of the patient. Common treatments for pancreatic cancer include:
- Surgery: If the cancer is caught at an early stage, surgery may be performed to remove the tumor and any affected lymph nodes. The type of surgery will depend on the location and size of the tumor. The surgery for pancreatic cancer depends upon the location of tumor. For cancers of pancreatic head a Whipple operation also known as pancreaticoduodenectomy is done. For cancer of body of pancreas distal pancreatectomy is done.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It may be given before or after surgery, or in combination with other treatments.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It may be used before or after surgery, or in combination with other treatments.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that target specific genes or proteins that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. This type of treatment may be used in combination with other treatments.
-
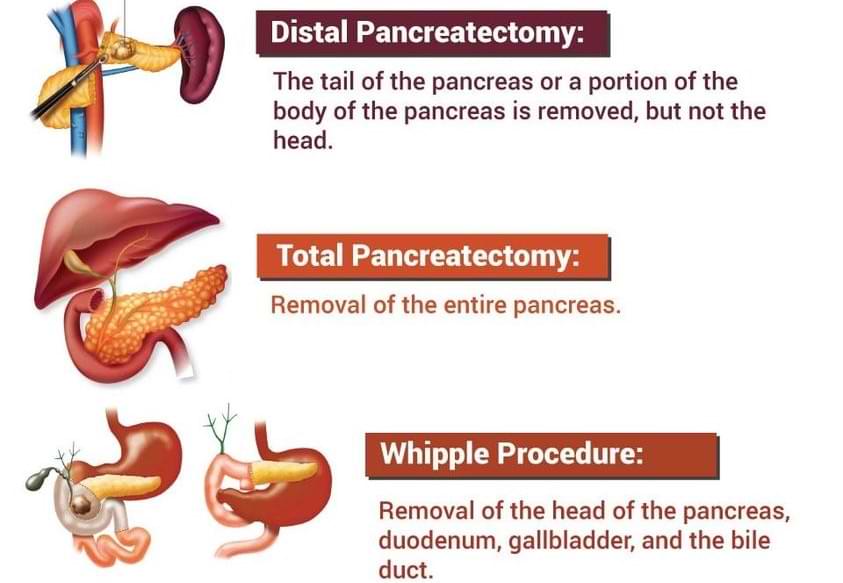
What type of surgery is typically performed for pancreatic cancer?
The type of surgery performed for pancreatic cancer depends on the location and size of the tumor. Some common surgical procedures for pancreatic cancer include:
- Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy): This is the most common surgery for pancreatic cancer. It involves removing the head of the pancreas, part of the small intestine, the bile duct, and sometimes part of the stomach.
- Distal pancreatectomy: This surgery involves removing the tail and body of the pancreas.
- Total pancreatectomy: This surgery involves removing the entire pancreas, as well as the spleen and part of the small intestine.
- Enucleation: This surgery involves removing only the tumor.
-
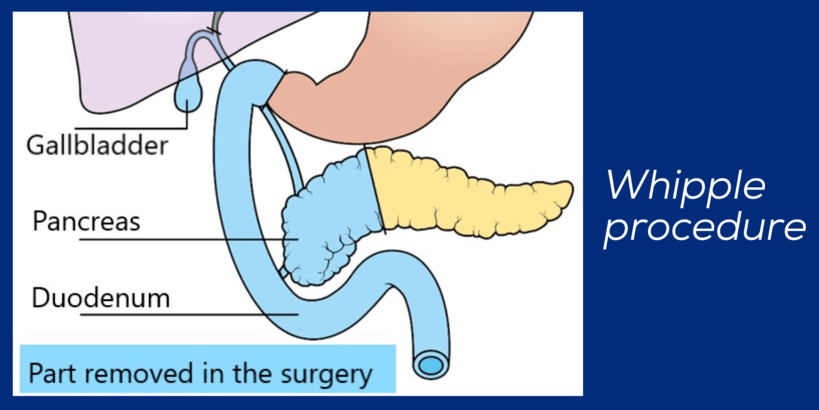
What is Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy) for pancreatic and periampullary cancer?
The Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy); is a surgical procedure used to treat pancreatic cancer and periampullary cancer. It involves removing the head of the pancreas, part of the small intestine, the bile duct, and sometimes part of the stomach. It is typically done for cancers that are located in the head of the pancreas and may be performed using open or laparoscopic surgery. The goal of the Whipple procedure is to remove the cancer and any affected lymph nodes. After the surgery, patients may need to undergo chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The success of the procedure depends on the stage of the cancer at the time of diagnosis and the overall health of the patient.
-
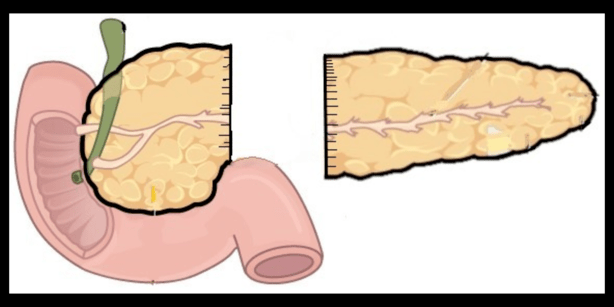
What is a distal pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer, pancreatic tumours and pancreatic cysts?
A distal pancreatectomy is a surgical procedure used to remove the tail and body of the pancreas in cases of pancreatic cancer, neuroendocrine tumours, and pancreatic cysts. The procedure may be performed using open surgery or laparoscopic surgery, depending on the specific needs of the patient. The purpose of the distal pancreatectomy is to remove the cancer or cyst and any affected lymph nodes. The outcome of the surgery depends on the stage of the disease and the overall health of the patient.
-

How to reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer
There are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer, including:
- Quit smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of pancreatic cancer. Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of developing the disease.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for pancreatic cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer. Avoiding processed and red meats, as well as foods high in saturated fat and sugar, can also help lower the risk.
- Avoid exposure to toxins: Exposure to certain chemicals and toxins, such as pesticides and air pollution, can increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Avoiding exposure to these substances can help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
By making lifestyle changes and being aware of potential risk factors, you can take steps to reduce your risk of pancreatic cancer.


